Wcf contains a great feature called queued services. This is basically a Wcf binding, netMsmqBinding, that uses MSMQ queues for message transport. It’s very easy to use (once set up) and allows for asynchronous and decoupled communication. It’s useful in several scenarios:
- Handling load peaks
- Robustness, if the service is down the messages are queued up in the MSMQ queue and are consumed by the service again when it’s available.
Requirements
The following is required for queued services to work
- MSMQ must be installed
- WAS must be enabled and running
- All service methods must be one-way
How it works
The client adds a service reference using a normal HTTP meta data endpoint and gets a reference to endpoints that are exposed with the netMsmqBinding. The client endpoint’s address is the MSMQ queue to post to in the following Uri format:
<endpoint address="net.msmq://localhost/private/myservice/myservice.svc" binding="netMsmqBinding" ... />
The client calls the client proxy just like for any other Wcf service:
var client = new MyService.MyServiceClient(); client.MyMethod(...);
The service is hosted in IIS and WAS (Windows Process Activation Service) is used for listening for messages in the queue. When a message is detected, WAS starts the IIS application containing the service that should receive the message. The service then consumes the message using the netMsmqBinding and processes it.
As already mentioned, the exposed service methods must be one-way:
[ServiceContract]
public interface IMyService
{
[OperationContract(IsOneWay = true)]
void MyMethod(...);
}
Throttling
If there are many messages in the queue then our service will process many of them in parallel. I think the default number of simultaneous requests is 12 and this may be too much for our service if the reason we’re doing queued services is to handle peak loads. Luckily this is really easy to configure:
<behaviors>
<serviceBehaviors>
<behavior name="MsmqWithMex">
<!-- Expose metadata via HTTP GET. -->
<serviceMetadata httpGetEnabled="true"/>
<!-- At most 3 concurrent requests are allowed -->
<serviceThrottling maxConcurrentCalls="3" />
</behavior>
</serviceBehaviors>
</behaviors>
Note: Throttling is available in all Wcf bindings, not just the netMsmqBinding.
Setting it all up
So far we have only discussed the implementation of the service, but we also have to do some configuration in the operating system and in IIS:
- Install Messaging – if this is not already done, then install it
- Create queue – Wcf relies on that the necessary queues exist. A good pattern is to check for their existence on application startup and create then if they’re missing.
- Install/configure WAS for MSMQ in IIS – This is probable the hardest step so I’ll describe in detail:
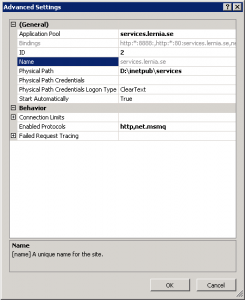
- Enable the net.msmq protocol for the site containing the service:
%windir%\system32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe set site "Default Web Site" -+bindings.[protocol='net.msmq',bindingInformation='localhost']
The result should be that “net.msmq” is included in the list of protocols:
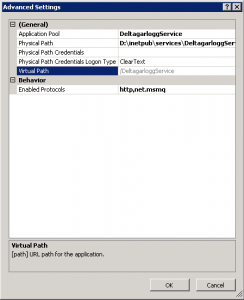
- We can also enable the same protocol in the single application containing the Wcf service:
%windir%\system32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe set app "Default Web Site/DeltagarloggService" /enabledProtocols:http,net.msmq
- Enable the net.msmq protocol for the site containing the service:
- Make sure that Net Msmq Listener Adapter service is running:

Troubleshooting
If something goes wrong, here are a few tips:
- Are the Message Queueing and Net Msmq Listener Adapter services running?
- net.msmq protocol enable on IIS site and application?
- Messages still in queue? If empty: check dead-letter queues and outgoing queues.
- Enable msmq journaling
- Check event log
- Restart app pool for the service
- Restart web site
- If queue is transactional, check the DTC
- Browse to the service’s svc file. If that consumes the messages it’s a WAS problem.
- If the service was hosted in Windows Server AppFabric, then see if it has any logged errors.
For more tips, Tom Hollander have written great blog posts about queued service here.
Happy queueing!
/Emil